通道表示与实体的开放连接,例如硬件设备、文件、网络套接字或能够执行一个或多个不同 I/O 操作(例如读取或写入)的程序组件。
1.1:Channel与Stream的对比
| Stream | Channel | 为什么 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 是否支持异步 | 否 | 是 | |
| 是否同时支持输入和输出 | 否 | 是 | Stream的输入、输出分别需要InputStream、OutputStream |
| 是否必须结合Buffer使用 | 否 | 是 | 缓冲区是通道内部发送数据和接收数据的端点 |
| 性能 | 低 | 高 | 通道是访问IO服务的导管,通过通道,我们可以以最小的开销来访问操作系统的I/O服务 |
1.2:Channel的类型
文件类:
- FileChannel
可通过 FileInputStream/FileOutputStream 的getChannel方法获取通道。
网络类:
面向流模式的socket协议:
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
可通过 Socket/SocketServer 的getChannel方法获取通道。
面向数据报模式的UDP协议:
- DatagramChannel
可通过 DatagramSocket 的getChannel方法获取通道。
1.3:操作系统IO演变史
早一代IO操作是由CPU负责IO接口: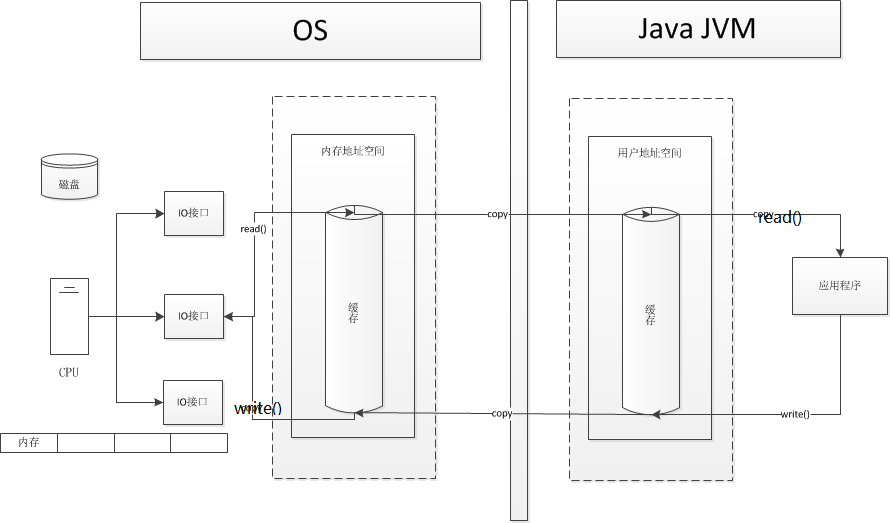
新一代DMA授权处理IO接口: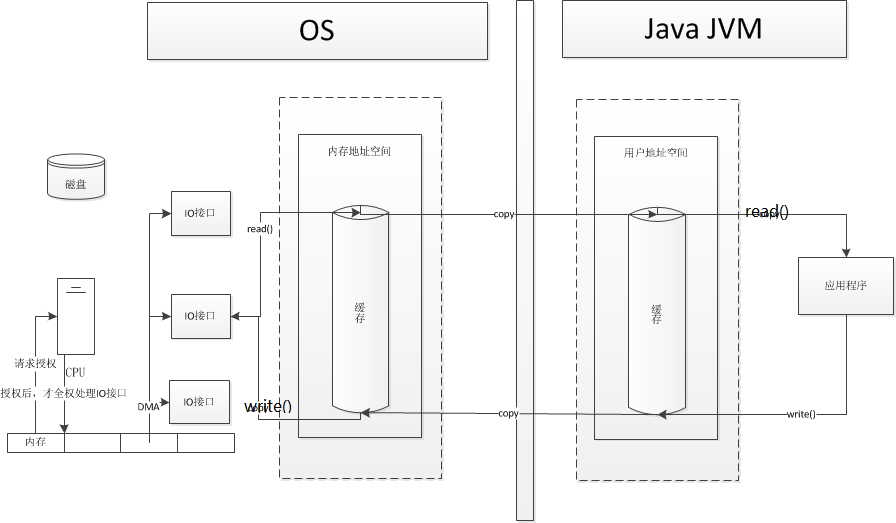
通道(Channel)模式: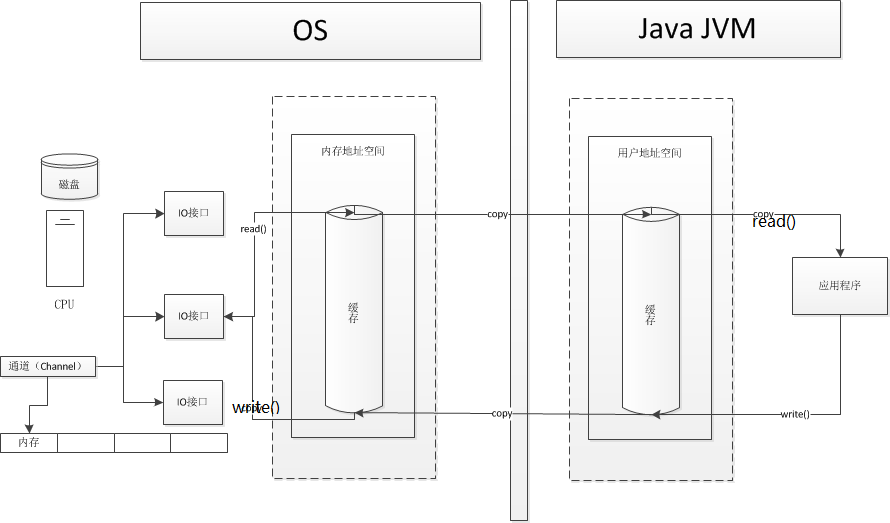
通道的产生是由于操作系统的升级而支持的。
在操作系统中对IO设备的控制方式一共有四种,按时间线依次是轮询、中断、DMA、和通道 方式。
- 轮旋
轮询就是进行IO时操作系统一直问控制器数据准备好了没有。
- 中断
中断就是异步的方式进行了,CPU向设备控制器发送一条IO指令后接着返回继续做原来的工作,而当设备控制器从设备中取出数据放到控制器的寄存器中后便向CPU发送中断信号,CPU在检查完数据后便向控制器发送取走数据的信号,将数据写入内存,但仍是以字节为单位的。
- DMA
DMA则是CPU和设备控制器之间的引入的一层加快速度的手段,由DMA代替CPU进行数据传送,CPU将指令发送给DMA,DMA向控制器发送请求,设备控制器将数据从缓冲区将数据直接写入内存。完成后设备控制器发送一个信号给DMA,DMA重复检查数据是否传送完成,确认完成后中断让CPU知道。
DMA比起中断方式已经显著减少了CPU的干预,但是CPU每发出一条IO指令,只能去读写一个连续的数据块,当要读多个数据块并存放到不同的内存区域中去,CPU需要发送多条IO指令及进行多次中断。
- 通道
IO通道方式是DMA方式的发展,把对一个数据块的干预减少为对一组数据块的干预。
IO通道有三种:
- 字节多路通道(Byte Multiplexor Channel)
- 选择通道(Block Selector Channel)
- 数组多路通道(Block Multiplexor Channel)
根据通道的工作方式分类,通道可以分为字节多路通道、选择通道、数组多路通道。
字节多路通道是一种简单的共享通道,主要用于连接大量的低速设备。
由于外围设备的工作速度较慢,通道在传送两个字节之间有很多空闲的时间,利用这段空闲时间字节多路通道可以为其他外围设备服务。因此字节多路通道采用分时工作方式,依赖它与CPU之间的高速总线分时为多台外围设备服务。
数据选择通道用于连接高速的外围设备。
高速外围设备需要很高的数据传输率,因此不能采用字节多路通道那样的控制方式。选择通道在物理上可以连接多台外围设备,但多台设备不能同事工作。也就是在同一段时间内,选择通道只能为一台外围设备服务,在不同的时间内可以选择不同的外围设备。一旦选中某一设备,通道就进入忙状态,知道该设备数据传输工作结束,才能为其他设备服务。
数组多路通道是字节多路通道和选择通道的结合。
其基本思想是:当某设备进行数据传输时,通道只为该设备服务;当设备在进行寻址等控制性操作时,通道暂时断开与设备的连接,挂起该设备的通道程序,去为其他设备服务,即执行其他设备的通道程序。有数数组多路通道既保持了选择通道的告诉传输数据的有点,又充分利用了控制性操作偶读时间间隔为其他设备服务,使得通道效率充分得到发挥,因此数据多路通道在实际计算机系统中应用最多,适合于高速设备的数据传输。(以上引用内容来源于百度教育)
至于JAVA的Channel和操作系统的的通道是如何选择通道类型、如何交互的就没法深入了,暂且理解JAVA的Channel是对操作系统的通道的一种抽象实现吧。
上一篇已经介绍过Channel的文件内存映射(map),就不做介绍了。
所谓的分散读取、聚集写入就是用多个buffer来接收数据、传输数据。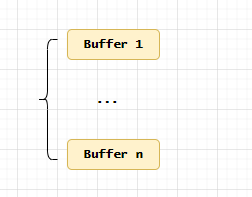
分散读取、聚集写入代码示例:
@Test public void gatherWrite() { FileInputStream inputStream = null; FileOutputStream outputStream = null; FileChannel inChannel = null; FileChannel outChannel = null; try { File file = new File("src/test/java/com/loper/mine/SQLParserTest.java"); inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); inChannel = inputStream.getChannel(); ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(8); ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(15); ByteBuffer[] buffers = new ByteBuffer[]{buffer1, buffer2}; // 分散读取 inChannel.read(buffers); for (ByteBuffer buffer : buffers) { buffer.flip(); System.out.println(buffer.mark()); } File outFile = new File("src/test/java/com/loper/mine/1.txt"); outputStream = new FileOutputStream(outFile); outChannel = outputStream.getChannel(); // 聚集写入 outChannel.write(buffers); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (inputStream != null) inputStream.close(); if (outputStream != null) outputStream.close(); if (inChannel != null) inChannel.close(); if (outChannel != null) outChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }4.1:socket协议
这部分代码比较复杂,可以翻看我的github代码,这里就不坐介绍了。
地址:https://github.com/zgq7/devloper-mine/tree/master/src/main/java/com/loper/mine/core/socket/nio
4.2:UDP协议
UDP发送数据:
@Test public void send() { DatagramChannel channel = null; try { channel = DatagramChannel.open(); // 设置为非阻塞 channel.configureBlocking(false); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) { String nextLine = scanner.nextLine(); buffer.put(nextLine.getBytes()); buffer.flip(); channel.send(buffer, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8056)); buffer.clear(); if ("over".equals(nextLine)) break; } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (channel != null) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }UDP接收数据:
@Test public void receive() { DatagramChannel channel = null; try { channel = DatagramChannel.open(); // 设置为非阻塞 channel.configureBlocking(false); channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8056)); Selector selector = Selector.open(); channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); while (true) { int select = selector.select(); boolean exit = false; Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next(); if (selectionKey.isReadable()) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); channel.receive(buffer); buffer.flip(); byte[] data = new byte[buffer.limit()]; buffer.get(data); String str = new String(data); System.out.println("收到:" + str); if ("over".equals(str)) exit = true; } iterator.remove(); } if (exit) break; } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (channel != null) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }接收端接收数据并退出:
以上即为本文理论知识+代码实战全部内容。如有错误欢迎指正。
本文参考文章: